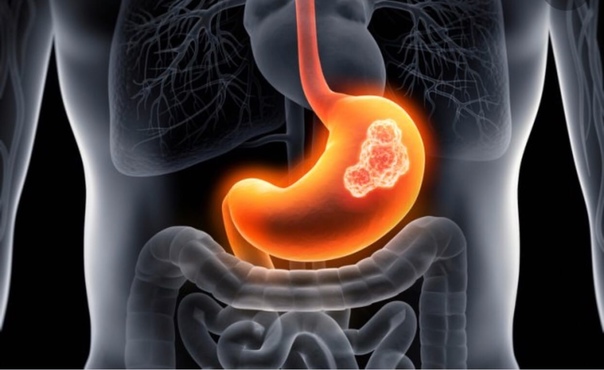
A gastrinoma, a tumor of the pancreas, can be benign or malignant, but it produces a hormone that causes stomach ulcers anyway.
What is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is the occurrence of one or more tumors in the head of the pancreas or small intestine. The disease is rare, occurs in one person in a million. Mostly men aged 20-50 are sick.
Tumor growth begins in the islet cells of the pancreas. Neoplasms can be both malignant and benign. The essence of the syndrome is that they produce gastrin, a hormone that stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach wall. Excess acid leads to stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Causes and risk factors for the development of the disease
The exact causes of the syndrome are still unknown. Scientists have found that in 20-30% of patients, gastrinomas are combined with a hereditary genetic disease. This condition is known as type I multiple endocrine neoplasia or MEN-I. With this pathology, tumors are found not only in the pancreas, but also in the parathyroid glands, in the pituitary gland.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome code according to ICD-10
The disease has a code E16.8, i.e. “Other specified disorders of pancreatic endocrine secretion”.
Symptoms and Signs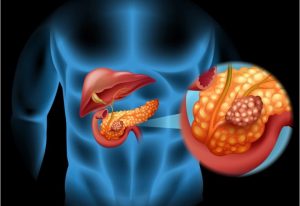
The symptoms of the disease are very similar to the manifestations of gastric ulcer. It is a dull, burning pain in the area between the navel and the sternum. It occurs between meals and at night, i.e. when the stomach is empty. The pain lasts from a few minutes to a few hours, then goes away.
Also, manifestations of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome can be:
diarrhea
bloating (flatulence)
discomfort in the upper abdomen. The patient gets the impression that “under the spoon” someone is “gnawing”. There may also be a feeling that it is burning or baking above the navel.
belching sour
heartburn.
Somewhat less often there are bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract, unexplained weight loss, decreased appetite. Sometimes the disease manifests itself only as diarrhea.
Diagnostic methods
Family history is very important to diagnose this rare condition. Therefore, a gastroenterologist asks about inherited diseases. If a relative has multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), the risk is increased. Also, the doctor finds out the patient’s complaints, specifies the nature and time of the onset of pain, the presence of other reactions from the gastrointestinal tract. Then the gastroenterologist examines, palpates (probes) the abdomen.
Blood tests for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
For accurate diagnosis, the content of gastrin in the blood is determined. An elevated level may indicate a tumor in the pancreas or duodenum. “High” gastrin may be a reaction to antiulcer drugs, such as proton pump blockers. Therefore, before taking a blood test, you need to inform your doctor about all chronic diseases and medications taken.
In unclear cases, a second measurement is carried out after stimulation with secretin: the hormone secretin is injected, then the gastrin level is determined again. In gastrinoma, it grows significantly after stimulation.
Instrumental examination methods
Measurement of acidity level. Gastric juice for analysis is taken using a nasogastric tube – a thin rubber tube that is inserted into the stomach through the nose with anesthesia. High acidity levels may indicate Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Gastroscopy allows you to see the ulcers and take a fragment of the bottom of the ulcer for examination in the laboratory.
Endoscopic ultrasound: the probe is mounted on the endoscope. The study is carried out directly in the stomach, this increases the chances of detecting tumors.
Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy or octreotide scan. A radioisotope that is safe for the patient is injected into a vein. The substance selectively accumulates in tumor cells, so that they can be observed in a gamma camera. It helps to visualize tumors not only in the pancreas and duodenum, but also in other organs and systems.
Also, CT and MRI are used to diagnose gastrinomas.
Treatment for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Usually, treatment begins with drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid. Then an operation is performed and gastrinomas are removed.
If the tumors are multiple and cannot be removed surgically, chemotherapy is prescribed.
Medications
The most commonly recommended drug is proton pump inhibitors. These drugs interfere with the function of the proton pump in cells and decrease the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. As a result, the patient notes a decrease in abdominal pain and diarrhea. Use:
esomeprazole
lansoprazole
pantoprazole
omeprazole
dexlansoprazole.
If there are contraindications to the appointment of antiulcer drugs, use octreotide. This substance is similar in its action to the hormone somatostatin, it neutralizes the effect of gastrin.
In chemotherapy, the following are most often administered:
streptozocin
5-fluorouracil
doxorubicin.
Complications
bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract
perforation of the stomach or intestines with the development of peritonitis
weight loss
severe diarrhea
spread of the tumor to other organs.
Forecast
Complete cure is rare, even if the tumor is detected at an early stage. However, gastrinomas https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastrinoma grow very slowly and you can live with these tumors for many years.
Prophylaxis
There is no evidence in studies that diet, diet, or the use of any foods affect the development of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.